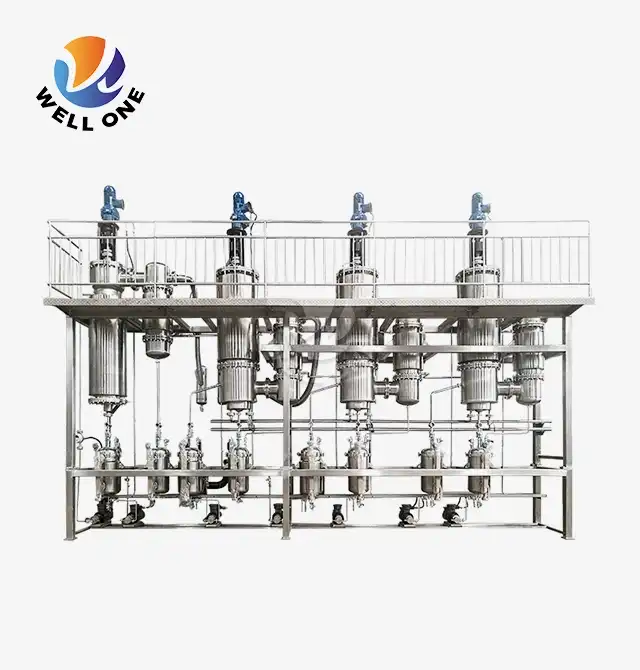
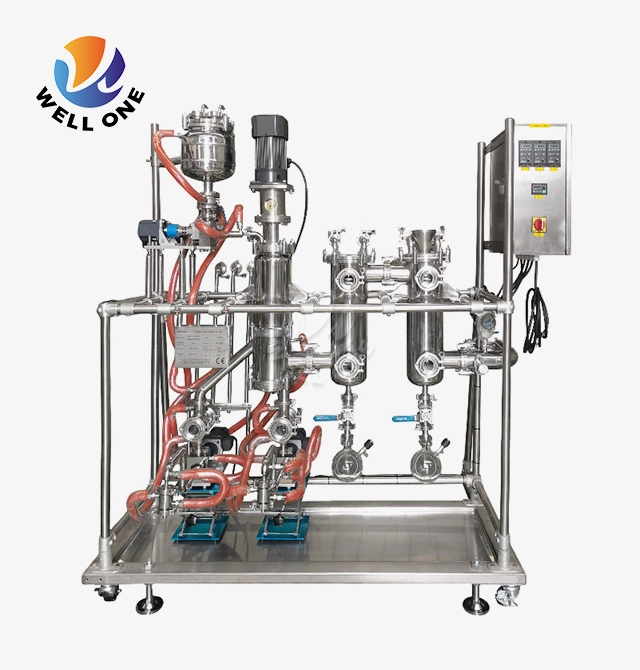
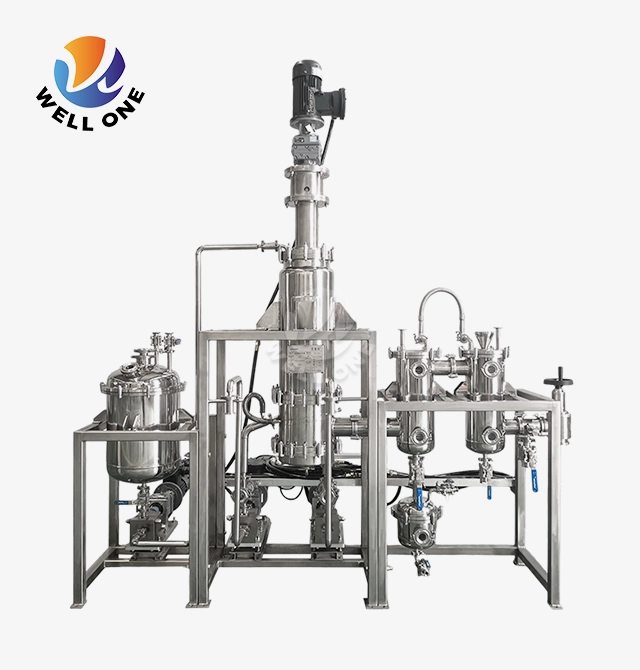
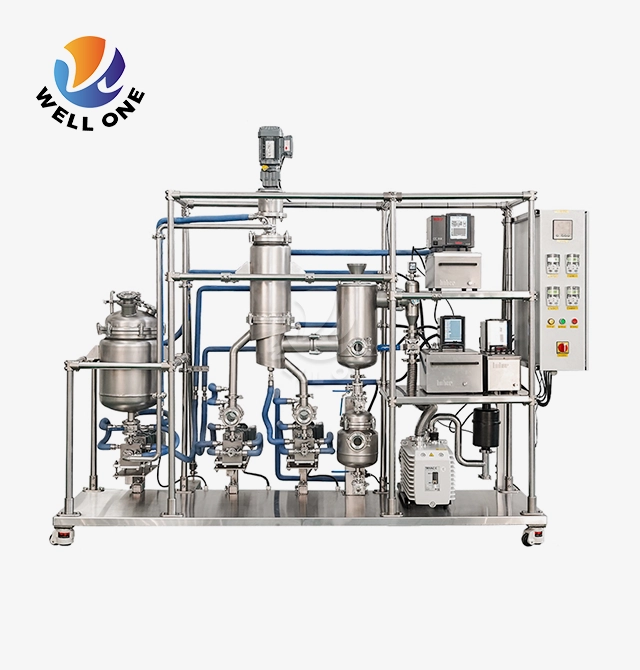
What Is Agitated Thin Film Evaporator?
Agitated thin film evaporators are a specialized type of equipment used in a variety of industrial processes to efficiently separate liquids from solids, liquids from liquids, or vaporize liquid solutions. In this equipment, liquids are distributed in the form of a thin film under vacuum conditions and are exposed to efficient heating and agitation mechanisms that accelerate the rate of evaporation.
Definition and Background
Agitated thin film evaporators, sometimes referred to as wiped film evaporators or ATFEs, are designed to facilitate evaporation and vaporization of liquids rapidly under vacuum conditions. They utilize the principles of thin film evaporation while enhancing the process through internal agitation or wiping mechanisms. This agitation promotes turbulent flow and helps expose the liquid to more surface area for increased evaporation.
Agitated thin film evaporators are used in many industries including chemical, pharmaceutical, food, wastewater treatment, and more. Their key purpose is to concentrate solutions, separate mixtures, crystallize solutes, recover solvents, and purify end products through highly efficient evaporation. Compared to conventional evaporators, ATFEs offer faster evaporation rates, shorter residence times, and the ability to process heat-sensitive materials.
Operating Principles
Overview of Thin Film Evaporation
Thin film evaporation refers to the process by which a liquid is introduced into an evacuated chamber in the form of a thin film. The large surface area to volume ratio of the thin film allows for very rapid and efficient heat transfer and evaporation. This is in contrast to conventional evaporators where the liquid forms a deep pool and relies solely on conduction to deliver heat.
Some key principles of thin film evaporation are:
- High surface area contact with heating source
- Short diffusion distance for vapor molecules
- Low pressure operation (vacuum) reduces boiling point
- Short exposure time at elevated temperatures
- High heat transfer coefficients
- Rapid volatile component removal
Compared to conventional evaporators, thin film units can achieve up to 10 times higher evaporation rates due to these factors.
Agitation Mechanism
While thin film evaporation offers kinetic advantages, the process can be limited by fouling and concentration gradients building up in the liquid film. Agitation mechanisms are thus incorporated into agitated thin film evaporators to address these limitations.
Agitation enhances thin film evaporation in several ways:
- Prevents fouling and crust formation by continuously wiping the heat transfer surfaces
- Promotes turbulent flow which improves mixing and heat transfer
- Renews liquid film surface and breaks temperature gradients
- Allows handling of viscous, fouling, or crystallizing solutions
- Facilitates processing of highly concentrated solutions up to solid content
This agitation or wiping action significantly improves the overall efficiency and throughput of the equipment.
Design and Components
Equipment Structure
The main components of an agitated thin film evaporator are:
- Cylindrical evaporator body and jacket - Provides the containment vessel and houses the heating/cooling jacket. Typically made of stainless steel or exotic alloys.
- Rotor assembly - Houses the agitator blades, shaft, and bearings. Rotates at high speed to wipe the internals.
- Agitator blades - Shaped blades affixed to the rotor that wipe the internal surfaces. Different configurations optimize flow.
- Heating/Cooling jacket - Circulation of heating or cooling media to add/remove energy. Steam, thermal oils, chillers are commonly used.
- Vacuum system - Maintains low pressure in the evaporator body to allow low temperature evaporation.
- Inlet system - Distributes feed liquid evenly into a thin falling film. May use spray nozzles, flow distributors etc.
- Vapour outlet - Separates vapor from liquid and transports it out of the evaporator.
- Condensate outlets - Liquid product outlets for separating concentrates, condensates etc.
Heating and Cooling Methods
Agitated thin film evaporators utilize various heating and cooling techniques depending on the application:
- Steam - Most common heating method. Steam condenses in jacket and heats product film via conduction. Offers clean operation.
- Thermal oils - Used for heating above steam temperatures or for viscosity control. Circulated in jacket to deliver heat.
- Electric heating - Electrical elements immersed directly in product film. Allows precise temperature control.
- Chilled water - Water, brines or other coolants circulated in jacket for condenser operation.
- Refrigerants - Direct refrigerant evaporation in jacket used for sub-ambient or cryogenic operation.
Proper heating/cooling selection considers required temperature levels, safety, fouling risks, and compatibility with the product.
Applications and Industries
Chemical Industry
Agitated thin film evaporators are widely used in the chemical industry for concentration, purification, and separation of various inorganic and organic chemicals. Typical applications include:
- Concentrating acids, alkalis, and inorganic salt solutions
- Separating isomers and thermally sensitive materials
- Purifying monomers in polymer production
- Solvent recovery from chemical reactions and extractions
- Crystallization processes through controlled evaporation
- Processing corrosive, viscous, or fouling materials
The excellent heat transfer, short residence time, and wiping action make ATFEs ideal for the demands of chemical manufacturing. They allow product quality to be maintained even at high concentrations.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceutical production, agitated thin film evaporators serve key roles in APIs (active pharmaceutical ingredients) manufacturing including:
- Concentration and isolation of drug products from reaction mixtures
- Solvent recovery and reducing solvent levels in final APIs
- Purification of APIs through recrystallization
- Thermal and vacuum-controlled drying of API slurries
- Devolatilization and stripping unwanted volatiles
- Processing high viscosity, sticky, or fouling pharmaceutical slurries
ATFEs allow pharma manufacturers to achieve purity levels and environmental requirements through their selective evaporation capabilities.
Food Processing Industry
Agitated thin film evaporators provide an efficient method for concentrating and processing food products while retaining nutritional content:
- Concentrating fruit and vegetable juices while minimizing heat damage
- Removing undesirable odors and volatiles from food ingredients
- Recovering volatile aromas and essences from food liquids
- Processing high viscosity, particle laden, or sticky food materials
- Manufacturing shelf-stable and reconstitutable food concentrates
- Crystallization of food ingredients like sugars, fats, and flavors
The excellent heat transfer characteristics make ATFEs suitable for heat sensitive food ingredients. Their continuous operation also suits large-scale food production.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
Agitated thin film evaporators offer several advantages that make them a superior evaporation technology:
- Extremely high heat transfer coefficients due to thin film and turbulent flows
- Short product exposure times - seconds versus hours in conventional evaporators
- Ability to handle solutions up to very high concentrations near solid saturation
- Lower temperature operation due to efficient thermal profiles and vacuum operation
- High single pass yields and vapor stripping from agitation
- Lower fouling tendency compared to other evaporators
- Continuous and scalable operation suitable for large volumes
- Flexible configuration for multiple effects and vapor recompression
These benefits make ATFEs ideal for difficult separations or heat-sensitive materials.
Limitations
The limitations of agitated thin film evaporators include:
- Handling abrasive or particle laden feeds requires special metallurgy
- Requires experienced design to balance flow, residence time, and temperature
- More prone to mechanical failures compared to simple evaporators
- Initial capital investment is higher than basic evaporators
- Cleaning-in-place and maintenance requirements may be intensive
- Not suitable for forming dry crystalline solids or very thick pastes
Proper feed pre-treatment, equipment selection, and operation are key to minimizing these limitations.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-World Applications
Case 1: Solvent recovery in antibiotic production
An agitated thin film evaporator was implemented to recover solvents after an extraction step in an antibiotic manufacturing process. The ATFE allowed near complete recovery of the volatile solvent which was then condensed and recycled. This improved yields while meeting the strict environmental emissions targets.
Case 2: Algae oil concentration and extraction
A pilot scale agitated thin film evaporator was tested for concentrating algae slurries and extracting algae oil. The ATFE was able to process the high solids feed and raise oil concentrations to 20% for downstream extraction. Fouling was minimal compared to conventional evaporators.
Case 3: Freeze concentration of fruit juices
Multiple ATFEs were installed in a fruit juice plant to carry out freeze concentration. By operating the evaporators with chilled jackets, water was removed as ice to concentrate fruit flavors up to 65% solids. The process prevented degradation of heat-sensitive aromas.
In each case, the ATFE offered specific advantages that enabled difficult separations, kept product quality high, and improved process efficiency.
In Closing
Agitated thin film evaporators are highly specialized evaporation equipment that leverage thin films and agitation mechanisms to achieve extremely efficient separations and heat transfer. Their continuous operation, short residence times, and excellent thermal control make them ideal for products that are heat-sensitive, viscous, or fouling.
Though they require greater complexity in design and operation compared to simpler evaporators, ATFEs unlock significant advantages through their ability to process high concentrations and difficult applications. With a sound technical understanding and proper equipment selection, agitated thin film evaporators can serve as enabling technology across many industries and processes. Further research and consultation with experts is encouraged to fully explore the possibilities of these versatile evaporators.
Xi'an Well One Chemical Technology Co., Ltd is a leading provider of chemical equipment solutions with 17 years of experience. Our team of experts is dedicated to researching and producing innovative synthesis and purification separation equipment, and we offer comprehensive services to our customers. We provide a range of products such as molecular distillation devices and multi-level continuous-use systems, and our Agitated Thin Film Evaporator is a popular product. To learn more, visit our website or contact our sales team at Mobile: (+86) 18191320360 or Email: info@welloneupe.com.
References:
1. N?rv?nén, K., & Khlystov, A. (2019). Agitated Thin Film Evaporators for Efficient Liquid Separations. Processes, 7(2), 57.
2. Johnson, R. E. Mechanism and design of agitated thin-film evaporators for non-crystallizing, viscous, and fouling liquids. Dissertation, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, USA, 2017.
3. Mujumdar, A. S. (2019). Handbook of industrial drying. CRC Press.
4. Heidrich, B., & Fecher, P. (2017). Agitated thin film evaporators. In HANDBOOK ON NATURAL PIGMENTS IN FOOD AND BEVERAGES (pp. 337-351). Woodhead Publishing.
5. Sheikhzadeh, M. (Ed.). (2012). Solvent recycle and recovery. InTech.
6. Brennan, M. (2006). Food processing handbook. Wiley-VCH.
7. Geankoplis, C. J. (2018). Transport processes and separation process principles:(includes unit operations). Pearson Education India.