How is an Agitated Thin Film Evaporator Different from Other Types of Evaporators?
An agitated thin film evaporator is a specialized type of evaporator designed to efficiently separate liquid mixtures through evaporation. The primary purpose of evaporators is to concentrate liquid solutions by removing a portion of the solvent, typically water. This process finds widespread applications across various industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, food processing, wastewater treatment, and many others.
Overview of Different Types of Evaporators
Evaporators come in different plans and designs, each appropriate for explicit applications and working circumstances. Probably the most normally utilized evaporator types include:
Falling Film Evaporators: These evaporators depend on gravity to make a slim film of fluid on the intensity move surface. The liquid is distributed over the heating surface, and the thin film allows for efficient heat transfer and evaporation.
Forced Circulation Evaporators: In this sort of evaporator, a siphon is utilized to course the fluid through an intensity exchanger. The warmed fluid is then shipped off a separator, where the fume is taken out, and the concentrated fluid is recycled.
Multiple Effect Evaporators: These evaporators consist of a series of evaporator bodies, arranged in a way that allows the vapor from one effect to be used as the heating medium for the next effect. This design enables efficient energy utilization and can achieve high levels of concentration.
Explanation of Agitated Thin Film Evaporator
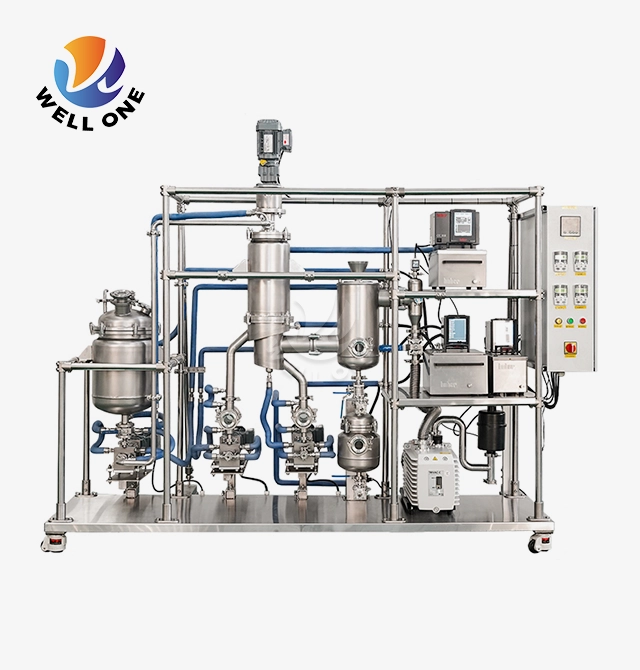
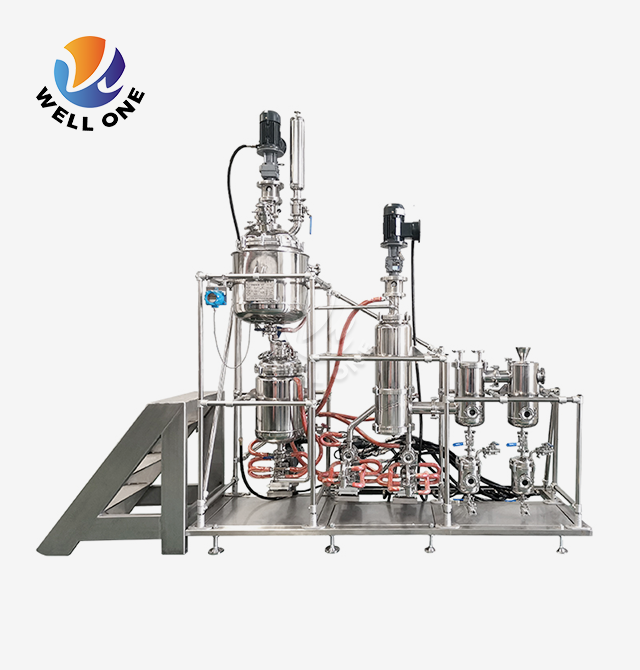
An agitated thin film evaporator, as the name suggests, is designed to create a thin liquid film on a heated surface through mechanical agitation. This special design integrates three principal parts:
Rotor: A round and hollow part that pivots at high velocities, normally going from hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute (RPM).
Stator: A stationary component that surrounds the rotor, providing a heated surface for evaporation.
Agitator Blades: Attached to the rotor, these blades create a thin liquid film on the heated surface of the stator, promoting rapid evaporation.
The liquid feed enters the evaporator and is distributed onto the heated stator surface by the rotating agitator blades. The mechanical agitation ensures the formation of a thin liquid film, which enhances heat transfer and evaporation rates. The generated vapor is then removed, leaving behind a concentrated liquid product.
Advantages of Agitated Thin Film Evaporators
Agitated thin film evaporators offer several advantages over other evaporator types, making them highly sought after in various industries:
Exceptional Heat Transfer Efficiency: The thin liquid film and high surface area exposure provided by the agitated design result in excellent heat transfer rates, leading to improved evaporation efficiency.
Minimal Residence Time: The continuous agitation and rapid evaporation minimize the residence time of the product in the evaporator, reducing the risk of product degradation and fouling.
Reduced Fouling and Scaling: The mechanical agitation helps prevent the build-up of scales and fouling on the heat transfer surfaces, ensuring consistent performance and longer operational cycles.
Versatility: Agitated thin film evaporators can handle a wide range of liquid materials, including viscous, heat-sensitive, and fouling-prone solutions, making them suitable for diverse applications.
Applications of Agitated Thin Film Evaporators
Agitated thin film evaporators find extensive applications in industries where high-quality product concentration or solvent removal is crucial:
Pharmaceutical Industry: These evaporators are used for the concentration of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), antibiotics, and other heat-sensitive pharmaceutical products.
Chemical Industry: They are employed in the production of specialty chemicals, resins, polymers, and other chemical compounds, allowing for efficient solvent removal and product concentration.
Food Processing Industry: Agitated thin film evaporators are utilized in the concentration of fruit juices, dairy products, and other heat-sensitive food materials, preserving their flavor and nutritional qualities.
Wastewater Treatment Industry: They are used for the removal of contaminants and recovery of valuable components from industrial wastewater streams, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Biofuel Production: These evaporators play a crucial role in the production of biofuels, such as biodiesel and bioethanol, by removing solvents and purifying the final product.
Comparison with Other Evaporator Types
When compared to other evaporator types, agitated thin film evaporators offer several advantages:
Falling Film Evaporators: Agitated thin film evaporators typically offer higher heat transfer rates and better resistance to fouling and scaling, making them more suitable for handling viscous or fouling-prone liquids.
Forced Circulation Evaporators: While effective for certain applications, forced circulation evaporators may have limitations in handling highly viscous or heat-sensitive materials, where the agitated thin film design excels.
Multiple Effect Evaporators: Although multiple effect evaporators are energy-efficient, they often require larger footprints and higher initial capital investments compared to agitated thin film evaporators. Additionally, the agitated design provides better control over product quality and residence time.
Case Studies or Examples
Several case studies have highlighted the successful implementation of agitated thin film evaporators in various industries:
Biodiesel Production: A case study published by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) demonstrated the use of an agitated thin film evaporator in the production of biodiesel. The evaporator effectively removed methanol from the biodiesel product, achieving high purity levels while minimizing energy consumption.
Fruit Juice Concentration: In the food industry, an agitated thin film evaporator was employed in the concentration of fruit juices, such as apple and orange juices. The evaporator preserved heat-sensitive compounds and flavors, resulting in high-quality concentrated juices.
Pharmaceutical API Concentration: A leading pharmaceutical company utilized an agitated thin film evaporator for the concentration of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The evaporator's gentle processing conditions and short residence time ensured the preservation of the API's potency and stability.
Limitations and Considerations
While agitated thin film evaporators offer numerous advantages, there are certain limitations and considerations to be aware of:
Initial Capital Cost: These evaporators typically have higher initial capital costs compared to some other evaporator types, due to their complex design and specialized components.
Maintenance Requirements: The rotating components and seals in agitated thin film evaporators require more frequent maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance and prevent leaks or failures.
Material Compatibility: The suitability of agitated thin film evaporators for specific applications should be carefully evaluated, considering factors such as viscosity, fouling propensity, and temperature sensitivity of the materials being processed.
Scale-up Challenges: Scaling up from laboratory or pilot-scale agitated thin film evaporators to larger industrial units can be challenging, requiring careful consideration of design parameters and operational conditions.
Emerging Trends and Future Developments
As industries continue to prioritize energy efficiency, product quality, and sustainable practices, the adoption of agitated thin film evaporators is likely to increase. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further improving the performance and versatility of these evaporators:
Advanced Materials: The use of advanced materials in the construction of agitated thin film evaporators can enhance their durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with a wider range of materials.
Process Intensification: Researchers are exploring ways to intensify the evaporation process through novel designs, such as integrating static mixers or incorporating advanced agitation mechanisms.
Automation and Control: The implementation of advanced automation and control systems can optimize the operation of agitated thin film evaporators, improving process efficiency, product quality, and overall performance.
Hybrid Evaporator Systems: Combining agitated thin film evaporators with other evaporator types or processes, such as membrane filtration or crystallization, can unlock new possibilities and enhance the overall efficiency of separation and purification processes.
Conclusion
Agitated thin film evaporators stand out among other evaporator types due to their unique design and operational principles. Their ability to create a thin liquid film through mechanical agitation results in exceptional heat transfer efficiency, reduced residence time, and minimized fouling. These advantages make them highly valuable for industries requiring high-quality product concentration or solvent removal, such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food processing, wastewater treatment, and biofuel production.
As industries continue to prioritize energy efficiency, product quality, and sustainable practices, the adoption of agitated thin film evaporators is likely to increase. Further research and development in this technology can unlock even greater potential and broader applications across various sectors, while addressing limitations and improving performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Xi'an Well One Chemical Technology Co., Ltd, an exclusive export agency authorized by NewSet, is a renowned Agitated Thin Film Evaporator manufacturer. With 17 years of production and manufacturing experience, we ensure the best quality of our products by choosing the finest raw materials and leveraging professional equipment and our research team. Our OEM & ODM services are backed by our 3D design engineers who can provide users with 3D animation design, tailoring the appearance of the equipment to user preferences. Our product line includes experimental level, pilot level, and industrial level molecular distillation devices, as well as multi-level continuous use systems. These products have been well received by customers from various countries. If you are considering purchasing related equipment, please feel free to contact us at Mobile: (+86) 18191320360 or Email: info@welloneupe.com. We look forward to cooperating with you.
References:
1. Delplanque, J. P., & Bensalem, R. (2004). Evaporation: Principles, types, and applications. Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology, 1, 1375-1393.
2. Khawam, A., & Flanigan, D. R. (2006). Solid-state kinetic models: basics and mathematical fundamentals. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110(35), 17315-17328.
3. Langrish, T. A., & Kockel, T. K. (2001). The use of moisture isotherms in describing moisture exchange in food materials. Food Australia, 53(8), 354-358.
4. Lewicki, P. P. (1998). Some remarks on rehydration of dried foods. Journal of Food Engineering, 36(1), 81-87.
5. Singh, R. P., & Heldman, D. R. (2009). Introduction to food engineering. Academic press.
6. Berk, Z. (2018). Food process engineering and technology. Academic press.
7. Gowariker, V., Krishnamurthy, V. S., Gowariker, S., Dhanorkar, M., & Paranjape, K. (2009). The fertilizer encyclopedia. John Wiley & Sons.
8. Narayanan, C. M., & Beschyotn, D. (2007). Plant & Process Engineering 360. Chemical Engineering Progress, 103(8), 27-32.
9. Sinnott, R. K. (2005). Chemical engineering design (Vol. 6). Butterworth-Heinemann.
10. Wilburn, D. R. (2012). Key evaporator technologies for cost-effective industrial wastewater treatment. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2012(11), 6689-6705.